Blockchain alternatives are a hot debate in the technology sector. Let’s review 4 different types of blockchain technology, top 5 blockchains and post blockchain era. What’s next after blockchain, do you think Is Hedera Hashgraph the future? We compared hashgraph vs blockchain and explained why hashgraph might be better than blockchain.
Table of Contents
Blockchain technology has accelerated significantly in recent years. There are many reasons why companies are implementing blockchain. The widespread use of blockchain technology in well-known cryptocurrencies is one of the factors driving its explosive rise.
Despite having many features, the technology has a scalability problem, a shortage of throughput as a result of the widespread use. Due to these restrictions, it takes a long time for blockchain transactions to be authenticated as they move through different nodes.
However, there are currently a number of blockchain alternatives that outperform blockchain in terms of performance. Meanwhile, let’s assume that blockchain’s technical constraints remain. In that situation, companies might also wish to choose these new alternative solutions and tools that will lower their expenses, make integrating systems easier, and streamline the development process.
While there are a ton of articles you can read that will tell you various things about the many blockchain alternatives, we have selected a few that you should look at and decide whether they are superior for yourself. But first, let’s discuss the blockchain alternatives briefly before digging in more details. You can also learn everything about blockchain developers by reading our detailed article.
What is blockchain?
Blockchain is a technology that functions as a database and chains together blocks of digital data to store it. Despite this, the way the data is organized still makes it different from the existing database.
The block serves as a data storage device. The newly received data is added to a fresh block. Once the block has been filled with data, it is chained with the one before it, establishing a chain of data that is linked in chronological sequence. Each block in this section will be unique from the ones before it.
Blockchain technology is best recognized for keeping track of transactions when it comes to cryptocurrencies, one of the more well-known uses for it, including Bitcoin, Ethereum, and others.

Data integrity is guaranteed by the blockchain. This data integrity feature gives us the reassurance that the data is secure, and it’s important to note that no third parties are involved in this process.
Additionally, the blockchain only serves to maintain and disseminate the data rather than update it in the case of the currently stored information.
It is therefore guaranteed that the information contained here will be secure since the records are not changed, removed, or destroyed. The information in the blocks is kept, and each time a new transaction occurs, it is permanently recorded alongside the previously stored data in the form of a record, making it impossible to undo. So now you are fully informed about what a blockchain is. Now let’s discuss the 4 different types of blockchain technology before we dig into blockchain alternatives.
What are the 4 different types of blockchain technology?
There are four types of blockchain structures.
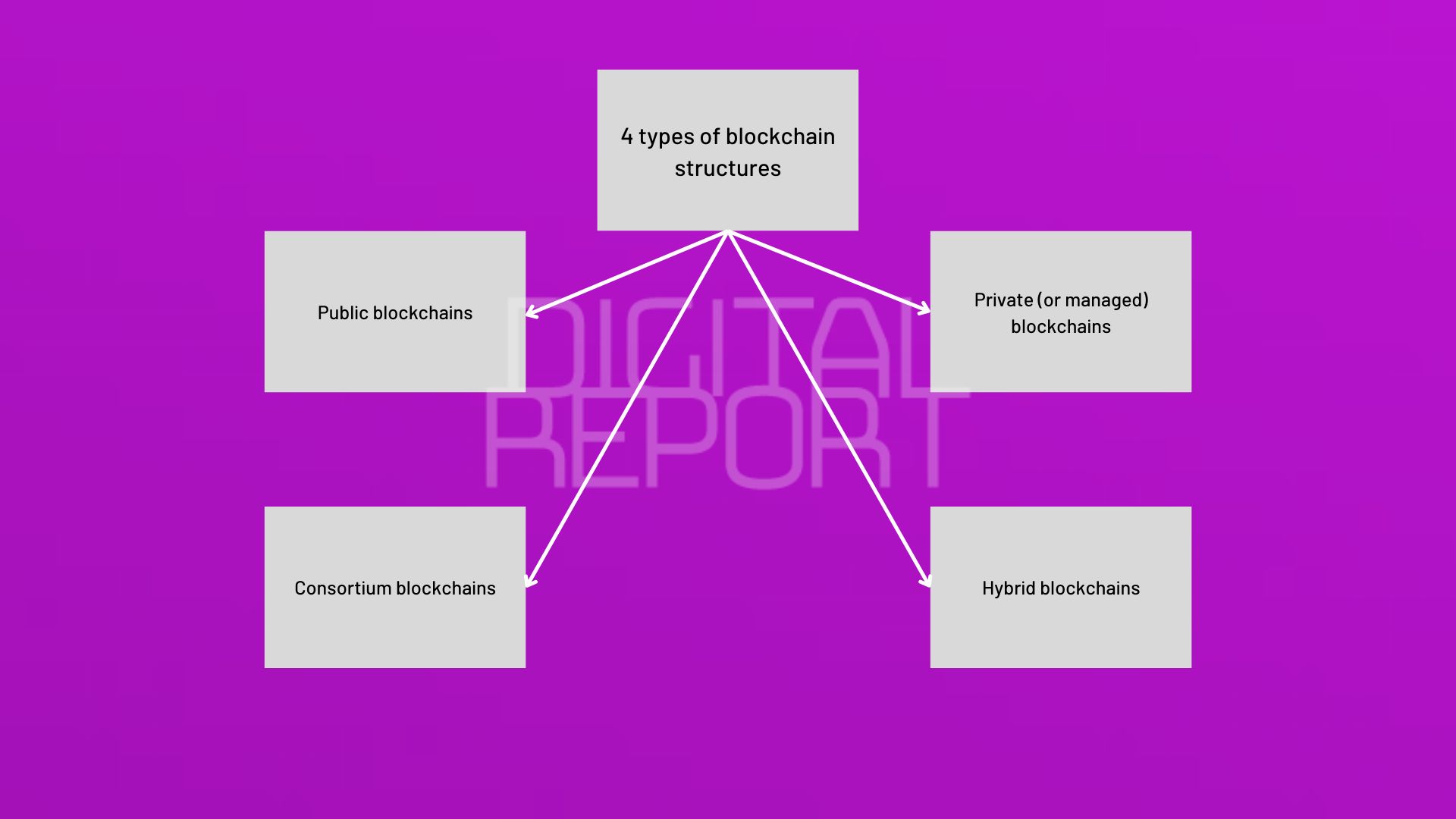
Public blockchains
Public blockchains are entirely decentralized, permissionless systems that anyone can join. Every node on a public blockchain has the same rights to access the blockchain, add new blocks of data, and validate existing blocks of data.
Public blockchains are largely utilized nowadays for bitcoin mining and trading. Popular public blockchains like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin may be familiar to you. The nodes “mine” for bitcoin on these open blockchains by constructing blocks for the network-requested transactions by resolving cryptographic puzzles. The miner nodes receive a little sum of cryptocurrency as payment for their laborious effort. The miners effectively take on the role of modern-day bank tellers who create a transaction and collect (or “mine”) payment in exchange.
Private (or managed) blockchains
Private blockchains, also known as managed blockchains, are permissioned blockchains under the management of a single company. Who is permitted to be a node on a private blockchain is decided by the central authority. Additionally, the central authority may not always accord each node an equal right to execute certain responsibilities. Due to restrictions on public access, private blockchains are only partially decentralized. The business-to-business virtual currency exchange network Ripple and the open-source blockchain application framework Hyperledger are two instances of private blockchains.
Both private and public blockchains have limitations; private blockchains are more susceptible to fraud and bad actors whereas public blockchains typically offer shorter validation times for new data. Consortia and hybrid blockchains were created to overcome these issues.
Consortium blockchains
Instead than being controlled by a single organization, as with a private blockchain, consortium blockchains are permissioned blockchains. As a result, consortium blockchains are more decentralized than private blockchains, which increases their security. But creating consortiums can be a difficult process because it calls for collaboration between several organizations, which poses logistical problems and a possible antitrust risk.
Additionally, some supply chain participants may lack the infrastructure and technology required to use blockchain technologies, and those who do may believe the upfront expenses are too high a price to pay in order to digitize their data and link to other participants in the supply chain.
The corporate software company R3 has created a well-known set of consortia blockchain solutions for the financial services industry and beyond. The Global Shipping Business Network Consortium was created by CargoSmart in the supply chain business. It is a non-profit blockchain consortium with the goal of digitalizing the shipping sector and enabling maritime industry operators to cooperate more effectively.
Hybrid blockchains
Blockchains that are managed by a single entity but have some oversight provided by the public blockchain, which is necessary to carry out specific transaction validations, are known as hybrid blockchains. IBM Food Trust is an illustration of a hybrid blockchain. It was created to increase efficiency along the entire food supply chain. It’s important to understand all blockchain types before getting deeper about blockchain alternatives.
What are the top 5 blockchains?
There are those who think differently, it is important which parameter we evaluate.
An open, decentralized public ledger is how blockchains were initially envisioned. We will keep to the original vision of blockchains as a public platform and omit permissioned blockchains from the list even if they presently exist in the market as private blockchain solutions and permissioned blockchains. The public blockchain is referred to as a permissionless blockchain as a result.
We’ll examine the top five blockchain protocols in this section before talking about blockchain alternatives. We can think of Blockchain protocols as the fundamental framework on which apps are constructed, and we stand to gain from any ecosystem expansion.
Bitcoin
The birth of Bitcoin in late 2008 served as the “founding father” of decentralized cryptocurrencies, helping to create the thriving ecosystem of coins and tokens that exists today. Oh, and it was essential in advancing the blockchain ledger’s use.
Therefore, it comes as no surprise that Bitcoin consistently ranks in the top 5 public blockchains.

The fundamental technology that underpins almost all of the cryptocurrencies we see today is similar to Bitcoin’s blockchain, despite the fact that Bitcoin serves as a medium of exchange rather than a blockchain protocol.
The advent of Bitcoin served as the catalyst for the entire cryptocurrency sector, and its blockchain serves as the benchmark for all other public blockchains. The distributed nature of the Bitcoin blockchain assures that there is no single point of entry, and the cryptographic features built into its blockchain mechanics guarantee that recording and storing data-related transactions is done in an incredibly secure manner.
Ethereum
On a list of the top 5 public blockchains, Ethereum comes in second.
Ethereum, a decentralized blockchain platform that was introduced in 2015, enables the development of Distributed Applications (Apps) and Smart Contracts without interruption, fraud, control, or intervention from outside parties.

Even though people are started looking for blockchain alternatives, its groundbreaking smart contracts technology makes it possible to create automated, self-executing contracts that have been pre-programmed.
The first decentralized blockchain to allow smart contracts, which have a wide range of real-world uses, is the Ethereum network.
Ethereum was created by Vitalik Buterin to broaden the uses for blockchain technology.
“Bitcoin is great as a form of digital money, but its scripting language is too weak for any kind of serious advanced applications to be built on top.”
–Vitalik Buterin, founder of Ethereum
NEO
With a focus on digitizing assets on the blockchain, NEO, originally known as Antshares, is a blockchain platform you may use to create a scalable network of decentralized applications.
The Chinese government’s far larger ambition to position itself as the leading force in the blockchain industry includes NEO, which is positioned as the first blockchain platform in China.
In contrast to Ethereum, NEO portrays itself as a project that focuses on the smart economy by encouraging the digitalization of real-world assets that allows for peer-to-peer network trade, clearing, and settlement as well as registration, depositary, transfer, and trading.
To put it another way, NEO aims to create a natural environment for the digital economy. The non-divisible NEO token, which creates and uses GAS tokens to pay for transaction fees created by applications on the network, is the native currency of the NEO blockchain.

The mining nodes for NEO’s Delegated Byzantine Fault Tolerance (dBFT) consensus method are selected by the NEO community and are subject to strict performance requirements as well as a requirement to hold a minimum number of NEO currencies.
The dBFT system has the advantage of using fewer resources than conventional consensus techniques while supporting a substantially larger volume of transactions, estimated at about 1,000 per second.
It does, however, come at the expense of centralization, where we are forced to put our faith in consensus nodes to act in the network’s best interests. That’s one reason behind why some people are looking for blockchain alternatives.
QTUM
The groundbreaking capabilities of Ethereum’s smart contracts and decentralized apps are combined with Bitcoin’s technological dependability to create QTUM, a hybrid platform that combines the best of both worlds (dApps).
It is a protocol that makes using smart contracts for business operations easier. Although QTUM is based on the Bitcoin source code (and so is a fork of Bitcoin), the development team has added some abstractions and layers on top of that to enable the inclusion of Ethereum’s smart contract features.

QTUM integrates a number of features from the two most popular cryptocurrencies—Bitcoin and Ethereum—in order to promote interoperability and benefit from their key features. The POS consensus method was successfully deployed for the first time by the QTUM blockchain technology. Since QTUM operates on a POS system, the native coin supply chains are unstable and inflate at a rate of 1% per year.
The QTUM blockchain can accommodate 60–70 transactions per second. It differs from other blockchain systems in that they emphasize the use of smart contracts for practical commercial applications.
WAVES
A decentralized blockchain network called WAVES focuses on giving users an easy-to-use interface for producing their own unique tokens.
Users may quickly start Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) and raise money for their projects by using WAVES without having to go through a technical learning curve. The many fiat currency connections in the WAVES platform’s native wallet are a standout feature that make it easy for users to convert cryptocurrency to fiat.

Technically speaking, WAVES is based on the Scorex modular platform, a system created to address numerous key problems with cryptocurrencies, including scalability, usability, and the usage of fiat gateways on the blockchain. Leased Proof-of-Stake is a different POS consensus algorithm that WAVES makes use of (LPOS).
Holders of WAVE tokens can participate in mining, safeguard the network, and earn extra coins by staking their coins thanks to LPOS. For holders, the mining and staking process is simple and effective. Users can trade their newly produced coin in a trading pair with any other WAVES coin on WAVES’ own decentralized exchange (DEX), which is another feature.
WAVES is capable of supporting 100 transactions per second at the moment.
Check out our top 5 blockchain platforms to consider in 2022 article to find out more details about this topic. In summary, these are our selections:
- Ethereum: Ethereum is one of the most established, oldest, and leading blockchain systems.
- Ripple: Ripple is concentrating its efforts on the platform’s development of financial applications.
- Cardano: Cardano is a smart contract-based next-generation blockchain platform.
- Stellar: Stellar is an open network blockchain that is used in the financial industry.
- Hyperledger Fabric: Hyperledger Fabric’s adaptable and modular designs are valuable in a variety of industrial applications.

The cryptocurrency sector is still in its infancy and is continuously changing. Adoption of blockchain technology is quickly gaining ground among consumers as well as in business and government settings. Blockchain will soon modernize capital markets and overtake other technologies as the world’s leader in technology.
The top 5 public blockchains that everyone needs to be aware of are ranked according to how widely they are used and how useful they are to the larger crypto community. The market leader is Bitcoin, and numerous other publicly available blockchain alternatives have developed over time to provide various utilities and use cases.
The numerous technological advancements made here will only improve with time as upgrades and revisions are made.
How many cryptos have their own blockchain?
There are currently more than 12,000 cryptocurrencies, and the growth rate is simply astounding. Between 2021 and 2022, the number of cryptocurrencies more than doubled. The market was adding roughly 1,000 new cryptocurrencies each month at the end of 2021.
Not all of this is good news. Investors must exercise caution because many new cryptocurrencies serve little purpose other than to generate revenue for their creators. Only a limited percentage of cryptocurrencies are worthwhile for research and possible purchase.

There are currently at least 1,000 blockchains and four different kinds of blockchain networks. Although the concept of a blockchain is a specific type of data transfer, this business offers a variety of platforms.
The supply chain, cryptocurrencies, decentralized exchanges, smart contracts, central bank money, and many other solutions utilise it. Thus, it applies to more than simply cryptocurrencies.
With 12,000 active cryptocurrencies built on the blockchain infrastructure, there are an increasing number of active blockchains. There are countless additional non-cryptocurrency blockchains to take into account.
What is the biggest blockchain company?
IBM, a cloud platform and cognitive solutions provider that was founded in 1911, is the biggest organization in the world to adopt blockchain. More than 220 companies have benefited from IBM’s assistance in creating blockchain-based apps and data governance solutions. IBM is probably the biggest blockchain company of the world.
Who has the best blockchain technology?
It’s hard to choose who has “the best blockchain technology.” Because every enterprise has its own different approach into the sector. The blockchain sector is now a significant one that has given rise to numerous billion-dollar ventures. Let’s look at the leading businesses that are using blockchain and causing a stir in the sector.
Binance
The largest digital currency exchange platform in the world right now is Binance, which was established in 2017 by Chinese-Canadian businessman Changpeng Zhao. In March 2022, the company handled spot trade volumes totaling $490 billion, according to data from CryptoCompare. A large variety of cryptocurrency pairs are supported by Binance, which also provides a high level of security and liquidity.
According to estimates, Binance today manages at least half of the market’s assets, and its ecosystem includes services for wallets, blockchains, cryptocurrencies, and education. Additionally, Binance is the creator of the Binance Coin token (BNB), which fuels the ecology of the exchange. The cryptocurrency can serve as the foundation for both network transactions and many other situations.

Coinbase
Another well-known cryptocurrency exchange, Coinbase, offers financial infrastructures for the blockchain ecosystem, including technology and transaction services developed for the global crypto economy. Together with co-founder Fred Ehrsam, a former trader for Goldman Sachs, Brian Armstron, a former Airbnb engineer, started the business in June 2012.
Although businesses may rely on Coinbase for a wider range of blockchain solutions, including building crypto-based applications and securely accepting crypto assets as payment, customers can invest in, consume, store, and use cryptocurrency through the platform. The exchange also offers blockchain development services so that entrepreneurs can design their own cryptocurrency goods.

ConsenSys
Ethereum blockchain solutions are offered by ConsenSys. Joseph Lubin, a co-founder of Ethereum and the Ethereum Foundation, launched the business. The business is renowned for implementing Ethereum enterprise network solutions for illustrious clientele, including as governments, businesses, and non-profit organizations. These businesses can investigate blockchain-based models and secure their IT infrastructures with aid from ConsenSys. ConsenSys also maintains a competitive edge by providing a wide range of digital solutions in addition to blockchain development expertise.

Gemini
Gemini, one of the top cryptocurrency exchanges in the world, was established in 2014 by the well-known Winklevoss twins. This exchange provides a large selection of cryptocurrency trading pairs on a reliable platform. But Gemini has also grown in popularity as a platform for its custodial service aimed at individual investors.
According to New York Banking Law, the business qualifies as a fiduciary and qualified custodian, and it has a state-issued license to safeguard digital assets. Gemini also has $200 million in custody insurance coverage, but it doesn’t mean anything. Gemini earns a spot on our ranking of the best blockchain firms in 2022 due to its reputation as a reliable exchange and its status as the first business to provide regulated custodial services.

Chainalysis
A software business called Chainalysis offers blockchain data analysis to both corporate and public sector companies. As businesses use cryptocurrencies more frequently, the use of digital tokens is also coming under more scrutiny. As a result, businesses should seek to identify potentially complex problems and raise legal concerns.
One of Chainanalysis’ key offerings is blockchain-related compliance and investigative software, which helps businesses use decentralized technologies in the safest possible manner. The identification and prevention of illicit activity in the blockchain industry is a key component of its solutions. Around 650 enterprises globally, including major banks, cryptocurrency exchanges, and payment processors, trust Chainalysis as one of the best blockchain platforms in the world.

Blockchain alternatives
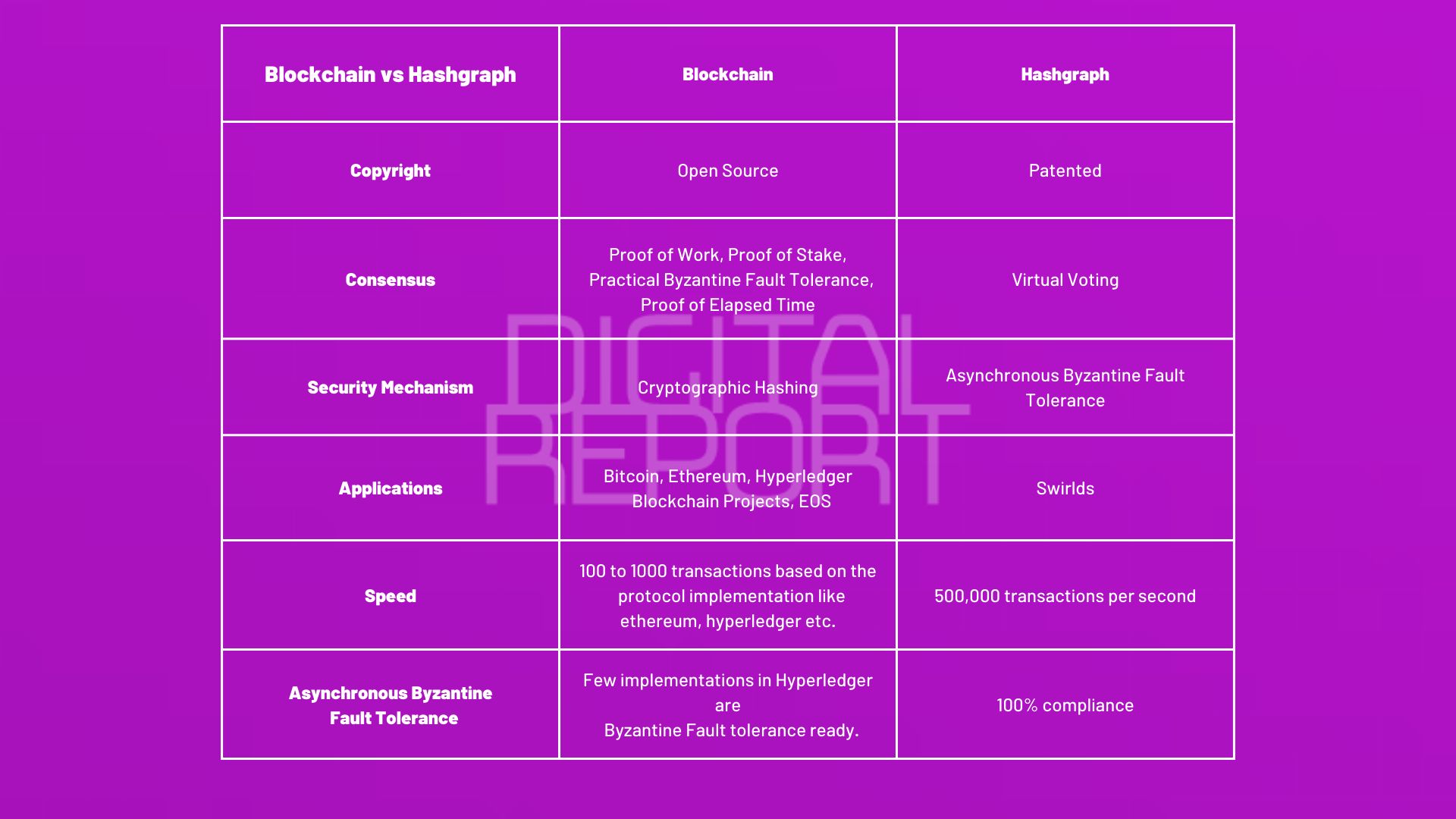
There certainly are blockchain alternatives. Consensus by effort has the drawback that, when more hardware is added, the network must operate more slowly in order to prevent forking, increasing transaction costs. BTC will never be widely adopted by merchants since it is built on a non-extensible architecture, whereas Visanet can do 65,000 transactions per second with a cheaper transaction cost. Although Hashgraph appears intriguing, it is not yet open source. The blockchain alternatives will be found in the next generation of DLT.
Post blockchain era
Just when you thought blockchain couldn’t be any more complicated, a variety of new cryptocurrencies and consensus algorithms that claim to outperform blockchain start to arise. They might represent the fourth wave of cryptocurrencies. We might need to forget all we’ve learned about blockchain, who knows.
What’s next after blockchain?
It is crucial to understand the impact of the metaverse on the real world before talking about potential future advances. Governments and large tech companies are both heavily investing in the metaverse. Blockchain technology and AR/VR accessories are used in the technology fusing the real and virtual worlds. Although it is still a developing technology, the excitement is real. One of the biggest investors is Meta (previously Facebook), which has $10 billion. Additional significant players include Microsoft, Nvidia, Epic, Roblox, and others.

A full-fledged metaverse metropolis was being built, among other multibillion dollar investments, during the most recent LEAP technology meeting in Riyadh. Blockchain powers the technology, while cryptocurrencies drive the metaverse economy. Future predictions point to a future that is even more promising, with the marketing sector predicted to reach over $800 billion by 2024.
Metaverse applications
Given that a metaverse might contain any element present in the real world, its potential uses are almost endless. Here are a few succinct examples:
- Virtual workplaces: The metaverse can provide a virtual 3D office setting where the staff can work from the comfort of their homes, perhaps donning hip and cool avatars. Microsoft Mesh and Facebook Horizon Workrooms are two examples that are currently available, however considerable work remains.
- Meta-education: The metaverse, which is already in various phases of development, can give students a more immersive educational experience across space and time.
- Real estate: Even without the potential buyer physically present in front of the for sale property, Metaverse can offer an immersive 3D virtual home tour.
- Virtual shops: Any product that is sold in physical locations can be included in the metaverse, giving customers a better viewing and estimation experience.
Is there a better technology than blockchain?
The blockchain industry has experienced tremendous growth in recent years and has been developing ever since. A blockchain is one type of distributed ledger technology (DLT), and there are many others as well. Some of these promise to offer greater benefits than blockchain.
What is Distributed Ledger Technology?
DLT is a technical framework that enables communication among members on a network in order to reach consensus. Multiple entities can access and update records simultaneously in an unalterable and unchangeable manner.
The decentralized nature of DLT is its distinguishing characteristic. It allows users to safely conduct transactions through a digital database. In a distributed network, decision-making and transaction control are not under the control of a single entity. This method distributes power among the network as opposed to giving it to a single entity (person or organization). It simultaneously records transaction details in several locations.

A distributed ledger technology makes sure that every participant has a copy of their unchangeable data and that there is no central authority, ensuring the integrity, transparency, and security of transactions. Not all DLTs, it should be noted, have the same features.
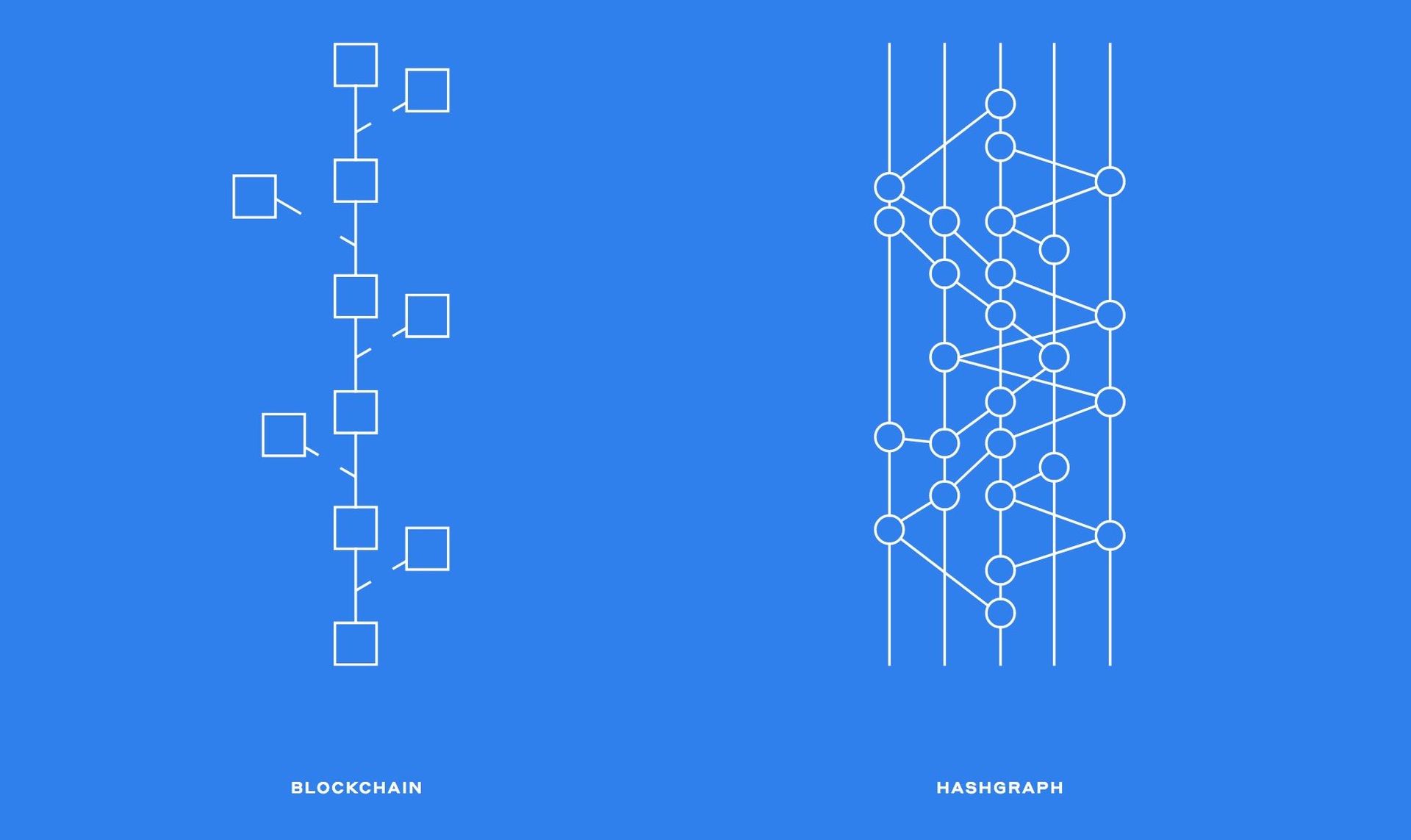
What is Hashgraph?
A lot of people see hashgraph as one of the biggest potential blockchain alternatives. Hedera or Hadera Hashgraph is a consensus algorithm that uses notions like virtual voting and chatter about gossip to facilitate quick and secure transactions. It makes the assertion that it fills the holes left by blockchain. Additionally, it is a peer-to-peer platform that does not require full transactional activities.
Since it can process tens of thousands of transactions per second and verify over a million signatures per second, Hashgraph is renowned for its speed. By demonstrating its value and legitimacy, it can be referred to as the new generation of blockchain and may very well replace blockchain technology.
Hashgraph employs a directed acyclic graph to help time sequence the transactions without breaking them into blocks rather than using miners to validate them. It uses the chatter about gossip protocol to transfer data between network nodes. The nodes circulate all the information around all the network participants by sending data to random nodes with the history of the previous transaction.
The cryptocurrency used by Hedera Hashgraph is called HBAR. Peer-to-peer payment systems, decentralized apps, the creation of micropayment systems, and network defense are all built using it.
Which crypto uses hashgraph?
Token holders can access distributed applications built on the Hedera Hashgraph platform using a utility token called Hbar. Cryptocurrencies, smart contracts, and distributed apps are made possible by the Hedera Hashgraph (DApps). Hedera uses a different proof-of-stake consensus method than other cryptocurrencies to offer quicker transaction speeds, fewer fees, and less energy consumption. It is owned and backed by some of the largest organizations in the world.
The Hedera project’s technology is open to developers looking for a more effective distributed ledger platform on which to launch their currencies, even though the number of cryptocurrency coins built on it is unlikely to ever match the numbers on more established blockchains.

By include Chainlink Labs on the Hedera Governing Council, the company has already taken steps to promote platform adoption by both currency developers and conventional financial services. This group is in charge of the Hedera network’s administration. It is crucial in determining whether outside businesses would use the platform as the foundation for their contemporary financial services.
One such business will introduce its AKTIO coin using the Hedera Token Service (HTS) technology. Automata ICO Ltd. This cryptocurrency is available via the akt.io platform, an application that intends to revolutionize the financial industry by enabling direct capital investments, automated investing using clever algorithms, and revenue production with digital assets. The preferred asset for services offered through the platform will be the AKTIO coin.
Hashgraph vs blockchain
Hbar is made to be quick, supports micropayments, and has affordable network rates. Additionally, users on Hedera Hashgraph receive Hbars as compensation for their participation in the network’s node launch. The cryptocurrency Hbar has a wide range of applications, including monetizing influencer and digital content.
Being software programs, smart contracts may also experience defects, erratic behavior under specific circumstances, and design flaws. The only way to change a smart contract once it has been released, whether to cure a bug or add new functionality, is to launch a new contract to replace the old one.
To enable “binding arbitration” for smart contracts, Hedera Hashgraph offers an optional mechanism. Hedera’s smart contract is unquestionably immutable, but if enough parties agree, the smart contract developer can make changes.
Developers can select the contract’s future mutability while deploying a smart contract on Hedera. Deploying a contract with a list of the public keys of the arbitrators is another option. Arbitrators would be given the ability to modify the contract’s code, add features, undo specific transactions, and address errors.
The Hedera Hashgraph, on the other hand, is a distributed ledger technology that utilizes the aforementioned data structure and a superior consensus process to provide the advantages of blockchain without its drawbacks.
The Hedera Hashgraph algorithm does not require Leader Based Systems or Proof of Work. It is capable of delivering excellent performance at low cost without having a single point of failure. Additionally, Hashgraph does not require a lot of computing power or electricity.
Is Hedera Hashgraph the future?
Some see Hedera Hashgraph as one of the most significant blockchain alternatives. In terms of transactions per second, every blockchain platform is different. For instance, the speed of transactions on Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Hyperledger Sawtooth can range from 7 to 10 per second for Bitcoin to up to 15 per second for Ethereum.
As information flows exponentially, Hedera Hashgraph permits hundreds of thousands of transactions per second.
Additionally, Hedera Hashgraph shows to be more equitable than blockchain due to the fact that miners can control the order of transactions, postpone them, or even prevent them from entering the block if necessary. Hashgraph, on the other hand, employs a consensus timestamp that prevents people from altering the order of transactions.
Although hashgraph is a promising technique, it has certain drawbacks. Only private and permission-based networks have the technology been used thus far. It has to be investigated and tested in a public network. When a node uses the Gossip about Gossip approach, there is a potential that the nearby nodes are malicious, which could stop information from reaching other nodes.
Although the Hedera Hashgraph’s technology is incredibly exciting, its whole potential and effectiveness won’t be realized until it is made available to the general public and non-permission-based networks.
Who has invested in Hedera Hashgraph?
The Hedera Governing Council, the group in charge of supervising platform governance, consists of over 17 corporations, including Tata Communications, Boeing, Google, IBM, LG Electronics, and Deutsche Telekom.
Users can issue and set up tokens on the Hedera platform via HTS, a Hedera network function. Hedera claimed that HTS, which is based on the recently established industry standard Token Taxonomy Framework from the InterWork Alliance, provides a quicker and more effective alternative to the generation of smart contract tokens.
More than 60 partners and users, including members of the governing council, initially endorsed the HTS.
Will hashgraph replace blockchain?
When talking about blockchain alternatives a lot of people are asking if hashgraph will replace blockchain. That’s somewhat debatable right now. While hashgraph has certain unique qualities that set it apart from blockchain, it also has significant drawbacks. According to what we have learned from the hashgraph engineers on the telegraph server, the system cannot scale very well above 1000 nodes. Hashgraph is constrained by the quantity of nodes required to transmit “gossip,” as opposed to blockchain, which is primarily constrained by the transaction rate.
We haven’t heard any specifics on how they want to handle that, despite the fact that they reportedly intend to use some form of “sharding” method. Sharding typically either necessitates the use of supernodes, which are able to view all transactions, or it sacrifices security by relying on nodes outside of the local shard group to report on transactions and state. If they have a miraculous way to circumvent those restrictions, we are not aware of it, and based on what we have learned, they haven’t actually developed anything substantial yet.
There is little doubt that hashgraph technology is ground-breaking, but it would be a bold assertion to say that it will outperform blockchain technology or make blockchains obsolete. Let’s examine what Hashgraph is capable of and what it is not.
Hashgraph’s proponents assert that it is faster than blockchain. Hashgraph has only been used on private networks up until recently, though. This technology’s potential in public networks hasn’t yet been investigated.
Why is hashgraph better than blockchain?
If we are talking about blockchain alternatives we also need to discuss the thesis of those who think hashgraph is better than blockchain.
- Since blockchain technology relies on proof-of-work, which consumes a significant amount of computational power, it is incredibly wasteful.
- Only 20 transactions can only be processed per second with the finest blockchain technology.
- More than 250,000 unconfirmed transactions have been backed up in Bitcoin, and the problem is just getting worse.
- The blockchain is an insecure It is essentially all vulnerable to attacks by quantum computers.
- Since every transaction must be carried around twice—once to get it on the network and once more to get the resulting block around—blockchain technology uses a lot of network capacity.
Hashgraph is at least as scalable as the “tangle,” which has demonstrated up to 1000 transactions per second using typical computers with typical network connections. Hashgraph does not require proof-of-work, is not vulnerable to quantum computer attacks, does not require doing anything unnecessary, passes data around only once (and with very little extra fluff), and does not require doing anything else.
It has all the benefits of the blockchain and the tangle while being safer, more effective, less wasteful, and more scalable.
What is Holochain?
When talking about blockchain alternatives, it’s hard to miss Holochain. An open source framework called Holochain is used to create completely distributed, peer-to-peer applications.
Holochain apps outperform blockchain in terms of flexibility, robustness, scalability, and efficiency by thousands of times (no token or mining required). So they can be count as blockchain alternatives too. The goal of Holochain is to make it possible for people to connect with one another by agreeing upon a common set of rules without depending on a central authority to impose or unilaterally alter those rules. Peer-to-peer interactions mean that you own and manage your data and that it is not collected, sold, or lost by a third party (such as Google, Facebook, or Uber).
Additionally, data ownership opens up new vistas for user agency and gives you more power over your data (imagine truly personal A.I., whose purpose is to serve you, rather than the corporation that created it). Composable and adaptable applications are made feasible by placing the user at the center.
Currency is optional in Holochain, unlike blockchains, which convert everything into tokens. Token issuance works best when it occurs as a result of peer activity (like ratings) or double-entry bookkeeping.
How to mine Holochain?
On Holochain, there’s no mining. Blockchain’s proof-of-work mechanism offers a large incentive for thousands of users to use their CPUs and GPUs, consuming enormous amounts of electricity, to process data for the sake of solving a pointless cryptographic puzzle.
Holochain does away with the requirement that all nodes be in synchronization with one another for global consensus. On Holochain, sharding is typically enabled. As a result, every time two nodes perform a transaction, a countersigned record of that transaction is saved by each node. The Distributed Hash Table is also updated with the transaction (sent to and saved by some unpredictably random nodes that can be looked up later for retrieval).

Sharding can be customized for each app, and sometimes it makes sense to disable it. Consider a distributed team communications system similar to Slack. Full synchronization would be worthwhile for the additional bandwidth required with only 40–50 members due to the advantages of offline communications and faster load times. Global synchronization isn’t actually necessary for the majority of workloads, hence sharding is still used.
The fact that Holochain doesn’t rely on the transport of a lot of redundant data and consumes a lot less bandwidth than blockchain is due to DHTs and the sharding they enable.
Conclusion
Demand for safe and affordable storage systems is rising as company data volume rises. Decentralized data storage systems that are highly secure, scalable, and economical have been made possible by blockchain technology. But the technology evolving and people already started looking for blockchain alternatives.
It might take some time for the technology to become widely accepted given how little it has developed compared to other fields. Even though the flaws are obvious, developers are still having trouble fixing them. Although this technology is only continuing to get better, the known advantages of decentralized storage attributed to blockchain currently outweigh those of conventional centralized storage systems. In summary, we have discussed following headlines:
- What is blockchain? Blockchain is a technology that functions as a database and chains together blocks of digital data to store it.
- What are the 4 different types of blockchain technology? Public blockchains, private (or managed) blockchains, consortium blockchains, hybrid blockchains. Details above.
- What are the top 5 blockchains? We have examined the top five blockchain protocols in this headline.
- How many cryptos have their own blockchain? There are currently at least 1,000 blockchains and four different kinds of blockchain networks.
- What is the biggest blockchain company? IBM, a cloud platform and cognitive solutions provider that was founded in 1911, is the biggest organization in the world to adopt blockchain.
- Who has the best blockchain technology? It’s hard to choose who has “the best blockchain technology.” Because every enterprise has its own different approach into the sector.
- Post blockchain era. The blockchain alternatives will be found in the next generation of DLT.
- What’s next after blockchain? It is crucial to understand the impact of the metaverse on the real world before talking about potential future advances.
- Is there a better technology than blockchain? A blockchain is one type of distributed ledger technology (DLT), and there are many others as well. Some of these promise to offer greater benefits than blockchain.
- What is Distributed Ledger Technology? DLT is a technical framework that enables communication among members on a network in order to reach consensus.
- What is Hashgraph? A lot of people see hashgraph as one of the biggest potential blockchain alternatives.
- Which crypto uses hashgraph? By including Chainlink Labs on the Hedera Governing Council, the company has already taken steps to promote platform adoption by both currency developers and conventional financial services.
- Hashgraph vs blockchain. HBAR is made to be quick, supports micropayments, and has affordable network rates. Details above.
- Is Hedera Hashgraph the future? In terms of transactions per second, every blockchain platform is different. As information flows exponentially, Hedera Hashgraph permits hundreds of thousands of transactions per second.
- Who has invested in Hedera Hashgraph? The Hedera Governing Council, the group in charge of supervising platform governance, consists of over 17 corporations, including Tata Communications, Boeing, Google, IBM, LG Electronics, and Deutsche Telekom.
- Will hashgraph replace blockchain? When talking about blockchain alternatives a lot of people are asking if hashgraph will replace blockchain. That’s somewhat debatable right now.
- Why is hashgraph better than blockchain? Since blockchain technology relies on proof-of-work, which consumes a significant amount of computational power, it is incredibly wasteful.
- What is Holochain? When talking about blockchain alternatives, it’s hard to miss Holochain. An open source framework called Holochain is used to create completely distributed, peer-to-peer applications.
- How to mine Holochain? There’s no mining on Holochain. Yet, it is seen as one of the greatest blockchain alternatives.










